Python Collections (Mappings & Streams)¶
Mappings¶
- A mapping is a mutable unordered collection of key/value pairs.
- Data structures implementing mappings, including associative arrays, lookup tables, and hash tables.
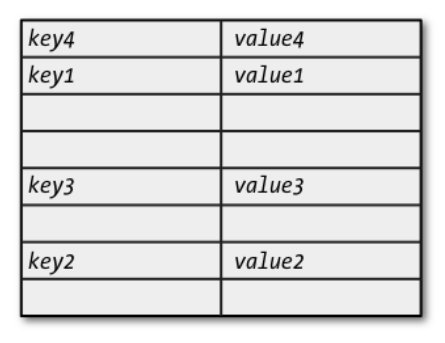
Dictionaries¶
- There is just one mapping type in Python:
dict, for "dictionary". dictcan be called with a collection argument to create a dictionary with the elements of the argument.- The elements must be tuples or lists of two elements - a key and a value:
dict((('A','adenine'),('T', 'thymine'), ('C','cytosine'),('G','guanine')))
- Dictionaries can also be written as a comma-separated list of key/value pairs enclosed in curly braces, with each key and value separated by a colon.
- Empty braces create an empty dictionary.
- The order within the braces doesn’t matter, since the dictionary implementation imposes its own order.
{'A': 'adenine', 'C': 'cytosine', 'G': 'guanine', 'T': 'thymine'}
- The keys of a mapping must be unique within the collection.
dictdoes not allow keys to be instances of mutable built-in types.
Dictionary example: RNA codon translation table¶
RNA_codon_table = {
# Second Base
# U C A G
# U
'UUU': 'Phe', 'UCU': 'Ser', 'UAU': 'Tyr', 'UGU': 'Cys', # UxU
'UUC': 'Phe', 'UCC': 'Ser', 'UAC': 'Tyr', 'UGC': 'Cys', # UxC
'UUA': 'Leu', 'UCA': 'Ser', 'UAA': '---', 'UGA': '---', # UxA
'UUG': 'Leu', 'UCG': 'Ser', 'UAG': '---', 'UGG': 'Urp', # UxG
# C
'CUU': 'Leu', 'CCU': 'Pro', 'CAU': 'His', 'CGU': 'Arg', # CxU
'CUC': 'Leu', 'CCC': 'Pro', 'CAC': 'His', 'CGC': 'Arg', # CxC
'CUA': 'Leu', 'CCA': 'Pro', 'CAA': 'Gln', 'CGA': 'Arg', # CxA
'CUG': 'Leu', 'CCG': 'Pro', 'CAG': 'Gln', 'CGG': 'Arg', # CxG
# A
'AUU': 'Ile', 'ACU': 'Thr', 'AAU': 'Asn', 'AGU': 'Ser', # AxU
'AUC': 'Ile', 'ACC': 'Thr', 'AAC': 'Asn', 'AGC': 'Ser', # AxC
'AUA': 'Ile', 'ACA': 'Thr', 'AAA': 'Lys', 'AGA': 'Arg', # AxA
'AUG': 'Met', 'ACG': 'Thr', 'AAG': 'Lys', 'AGG': 'Arg', # AxG
# G
'GUU': 'Val', 'GCU': 'Ala', 'GAU': 'Asp', 'GGU': 'Gly', # GxU
'GUC': 'Val', 'GCC': 'Ala', 'GAC': 'Asp', 'GGC': 'Gly', # GxC
'GUA': 'Val', 'GCA': 'Ala', 'GAA': 'Glu', 'GGA': 'Gly', # GxA
'GUG': 'Val', 'GCG': 'Ala', 'GAG': 'Glu', 'GGG': 'Gly' # GxG
}
def translate_RNA_codon(codon):
"""RNA codon lookup from a dictionary"""
return RNA_codon_table[codon]
translate_RNA_codon('GUG')
RNA_codon_table
- To obtain a function that will help you see the structure of your data, you should include the following line in your Python files:
from pprint import pprint as pp
pp(RNA_codon_table)

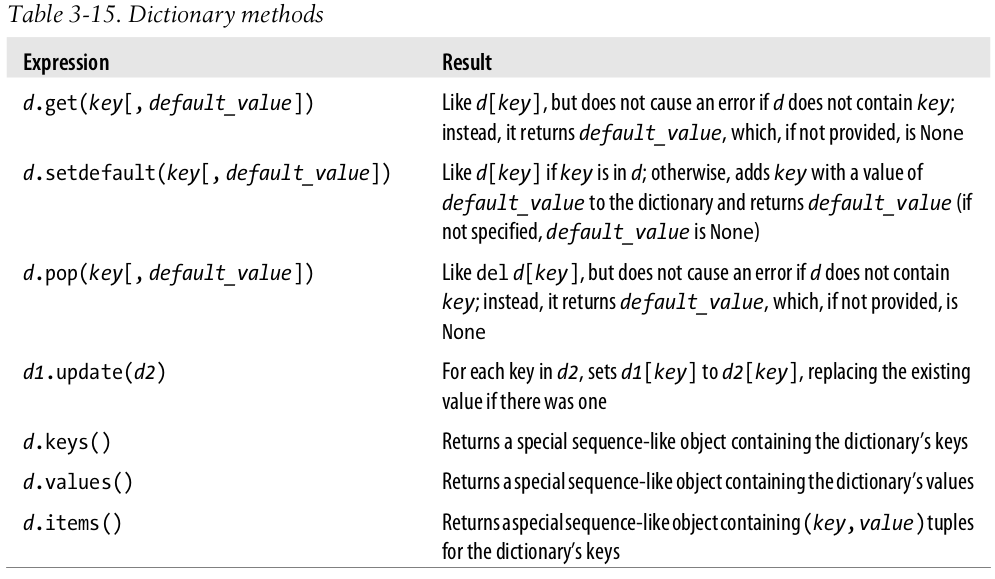
- Last three methods return "sequence-like objects": they aren't sequences, but they can be used as if they were in many contexts.
list(RNA_codon_table.keys())
Streams¶
- A stream is a temporally ordered sequence of indefinite length, usually limited to one type of element.
- Each stream has two ends: a source that provides the elements and a sink that absorbs the elements.
- The more common kinds of stream sources are files, network connections, and the output of a kind of function called a
generator. - Files and network sources are also common kinds of sinks.
Files¶
- A Python file is an object that is an
interfaceto an external file, not the file itself. - File objects provide methods for reading, writing, and managing their instances.
- Depending on a parameter supplied when an instance is created, the elements of the file object are either bytes or Unicode characters.
- Some methods treat files as streams of bytes or characters, and other methods treat them as streams of lines of bytes or characters.
- Most of the time a file object is a one-way sequence: it can either be read from or written to.
- It is possible to create a file object that is a two-way stream, though it would be more accurate to say it is a pair of streams—one for reading and one for writing—that just happen to connect to the same external file.
- Normally when a file object is created, if there was already a file with the same path that file is emptied.
- File objects can be created to append instead, though, so that data is written to the end of an existing file. #### Working with file objects
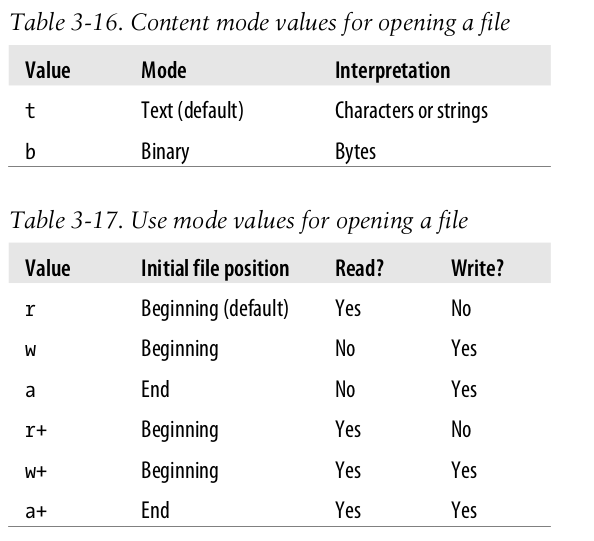
- built-in function
open(path, mode)creates a file object representing the external file at the operating system location specified by the string path. - The default use is reading, and the default interpretation is text.
- call the method
close()to close a file object when it’s no longer needed - The
withstatement is used to open and name a file, then automatically close the file regardless of whether an error occurs during the execution of its statements.with open(path, mode) as name:statements using name - More than one file can be opened with the same with statement, as when reading from one and writing to the other.
with open(path1, mode1) as name1, open(path2, mode2) as name2, ... :statements using names
File reading¶
fileobj.read([count])- Reads count bytes, or until the end of the file, whichever comes first; if count is omitted, reads everything until the end of the file. If at the end of the file, returns an empty string. This method treats the file as an input stream of characters.fileobj.readline([count])- Reads one line from the file object and returns the entire line, including the end-of-line character; if count is present, reads at most count characters. If at the end of the file, returns an empty string. This method treats the file as an input stream of lines.fileobj.readlines()- Reads lines of a file object until the end of the file is reached and returns them as a list of strings; this method treats the file as an input stream of lines.
File Writing¶
fileobj.write(string)- Writes string to fileobj , treating it as an output stream of characters.fileobj.writelines(sequence)- Writes each element of sequence , which must all be strings, to fileobj, treating it as an output stream of lines.
def read_FASTA_strings(filename):
"""Read FASTA sequence from a file"""
with open(filename) as file:
return file.read().split('>')[1:]
seqs = read_FASTA_strings("data/aa003.fasta")
seqs
- Problems with output:
- the description line preceding each sequence is part of the sequence string
- the string contains internal newline characters.
Generators¶
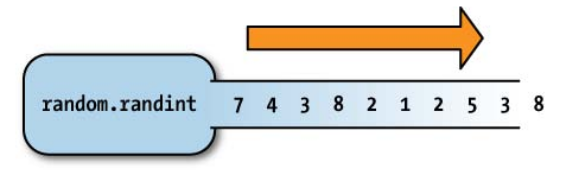
- A generator is an object that returns values from a series it computes. eg.
random.randint - Advantages of generators:
- A generator can produce an infinitely large series of values, as in the case of
random.randint - A generator can encapsulate significant computation with the caller requesting values until it finds one that meets some condition
- A generator can take the place of a list when the list is so long and/or its values are so large that creating the entire list before processing its elements would use enormous amounts of memory.
- A generator can produce an infinitely large series of values, as in the case of
- A value is obtained from a generator by calling the built-in function
nextwith the generator object as its argument. - The function that produced the generator object resumes its execution until a
yieldstatement is encountered. The value of theyieldis returned as the value ofnext. - The values of parameters and names assigned in the function are retained between calls.
next(generator[, default])- Gets the next value from the generator object; if the generator has no more values to produce, returnsdefault, raising an error if no default value was specified.
def genTest():
yield 1
yield 2
genTest()
foo = genTest()
foo.__next__()
for n in genTest():
print(n)
def genFib():
fibn_1 = 1 # fib(n - 1)
fibn_2 = 0 # fib(n - 2)
while True:
next = fibn_1 + fibn_2 # fib(n) = fib(n - 1) + fib(n - 2)
yield next
fibn_2 = fibn_1
fibn_1 = next
fib = genFib()
for i in range(10):
print(fib.__next__())
Comprehensions¶
- A comprehension creates a set, list, or dictionary from the results of evaluating an expression for each element of another collection.
- Each kind of comprehension is written surrounded by the characters used to surround the corresponding type of collection value: brackets for lists, and braces for sets and dictionaries.
List comprehensions¶
The simplest form of list comprehension is:
[expression for item in collection]
def validate_base_sequence(base_sequence, RNAflag = False):
valid_bases = 'UCAG' if RNAflag else 'TCAG'
return all([(base in valid_bases)
for base in base_sequence.upper()])
from random import randint
def random_base(RNAflag = False):
return ('UCAG' if RNAflag else 'TCAG')[randint(0,3)]
def random_codon(RNAflag = False):
return random_base(RNAflag) + random_base(RNAflag) + random_base(RNAflag)
def random_codons(minlength = 3, maxlength = 10, RNAflag = False):
"""Generate a random list of codons (RNA if RNAflag, else DNA)
between minlength and maxlength, inclusive"""
return [random_codon(RNAflag)
for n in range(randint(minlength, maxlength))]
minlength = 2
maxlength = 5
RNAflag = True
randnum = randint(minlength, maxlength)
randnum
[n for n in range(randnum)]
[random_codon(RNAflag) for n in range(randnum)]
def random_codons_translation(minlength = 3, maxlength = 10):
"""Generate a random list of codons between minlength and
maxlength, inclusive"""
return [translate_RNA_codon(codon) for codon in
random_codons(minlength, maxlength, True)]
random_codons_translation()
def test():
print()
print(random_base())
print(random_base())
print(random_base(False))
print(random_base(False))
print()
print(random_base(True))
print(random_base(True))
print(random_base(True))
print(random_base(True))
print()
print(random_codon())
print(random_codon(False))
print(random_codon(True))
print()
print(random_codons())
print(random_codons())
print(random_codons())
print(random_codons())
print()
print(random_codons(6))
print(random_codons(6, 15))
print()
print(random_codons(RNAflag = True))
print(random_codons(RNAflag = True))
print()
print(random_codons_translation())
print(random_codons_translation(5))
print()
print(random_codons_translation(8, 12))
print(random_codons_translation(8, 12))
test()
Revisit FASTA reader¶
- Suppose we want to split the description from a base sequence
def read_FASTA_entries(filename):
return [seq.partition('\n') for seq in read_FASTA_strings(filename)]
- Given a string
stringand another stringsepr, the callstring.partition(sepr)returns a tuple with three elements:- the part of string up to the first appearance of sepr
- sepr
- the part of string after sepr.
- Calling partition with an argument of
'\n'will split the description from the base sequence.
seqs = read_FASTA_entries("data/aa003.fasta")
seqs
- Next, we need to remove the newline characters from within each sequence string.
- Again, we’ll define a new function: it will use
str.replaceand another list comprehension. - We’ll also discard the useless
'>'that begins each description.
def read_FASTA_sequences(filename):
return [[seq[0], seq[2].replace('\n', '')] # delete newlines
for seq in read_FASTA_entries(filename)]
seqs = read_FASTA_sequences("data/aa003.fasta")
seqs
def read_FASTA_sequences_unpacked(filename):
return [(info, seq.replace('\n', ''))
for info, ignore, seq in # ignore is ignored (!)
read_FASTA_entries(filename)]
- The description lines of FASTA files generally contain vertical bars to separate field values.
- We define a new function that calls read_FASTA_sequences , then uses
str.splitto return a list of field values for the description instead of just a string.
def read_FASTA_sequences_and_info(filename):
return [[seq[0].split('|'), seq[1]] for seq in
read_FASTA_sequences(filename)]
seqs = read_FASTA_sequences_and_info(filename)
print(seqs)
- Each sequence in the result returned is represented by a two-element list.
- The first element is a list of the segments of the description
- The second is the whole sequence with no newline characters.
- Altogether, the functions we developed to read sequences from a FASTA file do the following:
- Split the file contents at '>' to get a list of strings representing entries
- Partition the strings to separate the first line from the rest
- Remove the useless '>' from the resulting triples
- Remove the newlines from the sequence data
- Split the description line into pieces where vertical bars appear
#Reading FASTA sequences with one compact function
def read_FASTA(filename):
with open(filename) as file:
return [(part[0].split('|'),
part[2].replace('\n', ''))
for part in
[entry.partition('\n')
for entry in file.read().split('>')[1:]]]
filename = 'data/aa003.fasta'
seqs = read_FASTA(filename)
seqs
Set & Dictionary Comprehensions¶
- Set Comprehension -
{expression for item in collection} - Dictionary Comprehension -
{key-expression: value-expression for key, value in collection}
def make_indexed_sequence_dictionary(filename):
return {info[3]: seq for info, seq in read_FASTA(filename)}
seqs = make_indexed_sequence_dictionary(filename)
seqs
Generetor expressions¶
- A 'generator expression' is syntactically like a list or set comprehension, except that it is surrounded with parentheses and its value is a generator:
(expression for item in collection)
### Generating amino acid translations of codons
def aa_generator(rnaseq):
"""Return a generator object that produces an amino acid by
translating the next three characters of rnaseq each time nextn
is called on it"""
return (translate_RNA_codon(rnaseq[n:n+3])
for n in range(0, len(rnaseq), 3))
seq = 'AUUCGAUCCGGACCCAUGAUCCCG'
print()
print(seq)
gen = aa_generator(seq)
assert 'Ile' == next(gen)
assert 'Arg' == next(gen)
assert 'Ser' == next(gen)
assert 'Gly' == next(gen)
assert 'Pro' == next(gen)
assert 'Met' == next(gen)
assert 'Ile' == next(gen)
gen = aa_generator(seq)
print(''.join(list(gen)))
Conditional Comprehensions¶
- One or more tests can be added to determine the elements for which the comprehension expression will be evaluated.
- This is called filtering and is implemented with a conditional comprehension
[expression for element in collection if test]
Extract just sequence descriptions from a FASTA file and split them into fields at their vertical bars.
### Reading FASTA descriptions from a file
def get_FASTA_descriptions(filename):
with open(filename) as file:
return [line[1:].split('|') for line in file if line[0] == '>']
print(get_FASTA_descriptions('data/aa010.fasta'))
### Reading FASTA descriptions using set comprehension (Read 3rd field)
def get_FASTA_codes(filename):
with open(filename) as file:
return {line.split('|')[3] for line in file
if line[0] == '>' and len(line.split('|')) > 2}
#print(get_FASTA_codes('data/BacillusSubtilisPlastmidP1414.fasta'))
print(get_FASTA_codes('data/aa010.fasta'))
### Constructing a selective dictionary
def make_gi_indexed_sequence_dictionary(filename):
return {info[1]: seq for info, seq in read_FASTA(filename)
if len(info) >= 2 and info[0] == 'gi'}
print(make_gi_indexed_sequence_dictionary('data/aa003.fasta'))
### Using a generator to find the first common element
def first_common(collection1, collection2):
"""Return the first element in collection1 that is in collection2"""
return next((item for item in collection1 if item in collection2), None)
print(first_common(range(1,22, 5), range(0, 22, 4)))
Nested Comprehensions¶
- Comprehensions can have more than one for in them. When they do, the innermost ranges over its collection for each of the next one out’s collection, and so on.
- It is rare to see more than two for sections in a comprehension, but occasionally three can be useful.
### A nested comprehension for generating codons
def generate_triples(chars='TCAG'):
"""Return a list of all three-character combinations of unique
characters in chars"""
chars = set(chars)
return [b1 + b2 + b3 for b1 in chars for b2 in chars for b3 in chars]
print(generate_triples())
print(set(generate_triples()))
Functional Parameters¶
- We will discuss the the
keyparameter associated with few functions & methods ####keyparameter
max(range(3, 7), key=abs)
max(range(-7, 3))
max(range(-7, 3), key=abs)
The value of the key argument is called on each element of the collection.
Consider a list seq_list containing RNA base sequences. We could select the sequence with the lowest GC content by calling min with key = gc_content.
The method list.sort was described. It too can take an optional key parameter - the value of key is called on each element, and the elements of the list are sorted according to the values returned.
lst = ['T', 'G', 'A', 'G', 't', 'g', 'a', 'g']
lst
lst.sort()
lst
lst.sort(key=str.lower)
lst
seqs = ['TACCTATACCGGCTA', 'cacctctaccgta', 'AACCTGTCCGGCTA']
seqs.sort()
seqs
seqs = ['TACCTATACCGGCTA', 'cacctctaccgta', 'AACCTGTCCGGCTA']
seqs.sort(key = str.lower)
seqs
Anonymous Functions¶
- functions and methods are objects that can be passed down as parameters
- The
defstatement creates a function object and names it. - There are many situations in which a functional parameter avoids a great deal of repetitive code.
- Python has a mechanism for defining lightweight functions without using
def. - These functions don’t have names - they are anonymous.
- Although they are functions, they are defined by an expression, not a statement. This kind of expression is called a lambda expression.
Syntax:lambda args: expression-using-args
def fn (x,y):
return x*x + y*y
fn = lambda x, y: x*x + y*y
### Definition of a function with a functional argument
def some(coll, pred=lambda x: x):
"""Return true if pred(item) is true for some item in coll"""
return next((True for item in coll if pred(item)), False)
print()
print('some(range(5)) is', some(range(5)))
print('some((None, '', 0)) is', some((None, '', 0)))
print('some(range(5), lambda x: x > 5) is', some(range(5), lambda x: x > 5))
print('some(range(5), lambda x: x > 3) is', some(range(5), lambda x: x > 3))
Sorting a list of strings in mixed case, suppose we want to order them by size first, and then alphabetically
l = [(3, 'abc'), (5, 'ghijk'), (5, 'abcde'), (2, 'bd')]
l.sort()
l
l = ['abc', 'ghijk', 'abcde', 'bd']
l.sort(key=lambda seq:(len(seq), seq.lower()))
l